21.2.1.4. Design Optimization Formulation
In order to help one’s understand for the design optimization terminology, let’s consider the following cantilever beam design shown in Figure 21.1. Suppose that the Load (P), material property (E) and the length (L) are fixed. In other words, those values cannot be changed during design process. These parameters are called ‘preassigned parameters’.
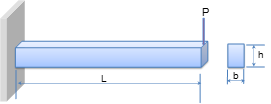
Figure 21.1 Cantilever Beam Design
Then, the designer wants to find the width (b) and the height (h) of beam section to satisfy the stress and deflection limitations (Sa,da). Also, for geometric limitation, the width and height have their lower and upper bounds (bL,bU) and (hL, hU). The former limitations for stress and deflection are ‘functional constraints’ and the latter limitations for design variables are ‘side constraints’.
Now, all design variable set, which satisfy these design constraints such as functional and side constraints, is a feasible design set. As you can see, there can be many feasible designs. Thus, the designer tries to find the design variables to minimize the mass of beam from the feasible set. Then, the final design is an optimum that minimizes the mass of beam while satisfying the stress, deflection and side constraints. In this case, the mass of beam is called ‘design objective’ or ‘objective function’.
Figure 21.2 shows the summary of cantilever beam design formulation. Sometimes, System Analysis requires complex CAE software. Mass, Stress and maximum deflection are called ‘analysis responses’.
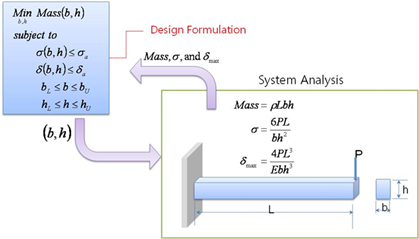
Figure 21.2 Design Optimization Formulation