21.2.3.5. DFSS/Robust Design Optimization
RecurDyn supports functions for the design for six sigma(DFSS) process. User can define random design variables from design variables and weightings on performance indices. For the detailed usage of DFSS and robust design, it is recommended that one reads Guides for Robust Design and DFSS in Guideline.
21.2.3.5.1. Run Step of DFSS/Robust Design Optimization
Select the DFSS/Robust icon of the Optimization group in the AutoDesign tab.

Figure 21.48 DFSS/Robust icon of the Optimization group in the AutoDesign tab
Define design variables with statistical information
Check design variables in the Design Variable page of the DFSS/Robust Design Optimization dialogue and define statistical information of design variables.
Variable Type: Design variable is defined and changed as a value between lower and upper bound during AutoDesign process. For the DFSS/Robust design optimization, it can be defined as random or deterministic variable. Standard deviation[SD] or coefficient of variation[COV] is defined to the random design variables. For the detailed information, one may refer to Random Variables in Guideline
Constant Type: Design variable is defined as a constant value. But the statistical definition is applied the constant type design variables like as variable types. For the detailed information for the usage of constant type, one may refer to Random Constants in Guideline.
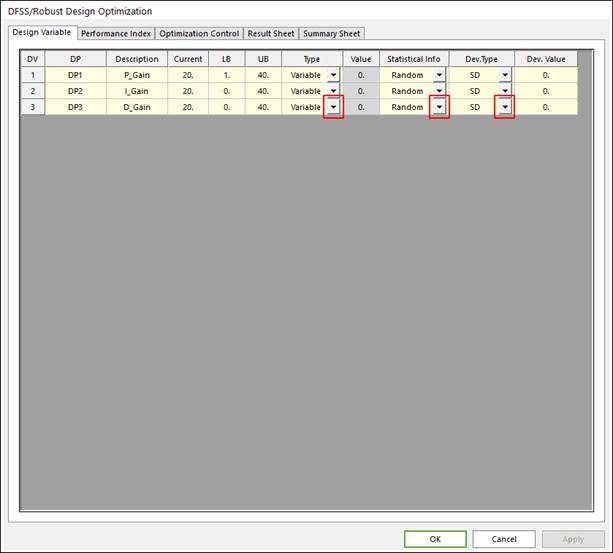
Figure 21.49 Design Variables tab of the DFSS/Robust Design Optimization dialog box
Formulate design optimization problem
The same step as the design optimization problem is applied to formulate DFSS/Robust design optimizations. Added index and weight values for DFSS/robust design are applied on each performance index. Refer to the Robust Design Optimization and Design For Six-Sigma (DFSS).
Objective function: Select definition type as Objective, and goal type as Min or Max. Next, define the weight value in Weight/Limit Value section. And define the robust index and Alpha weight.
Constraint condition: Select definition type as Constraint, and goal type as LE or GE or EQ. Next, define the limit value in Weight/Limit Value section. For the case of inequality constraint, the robust index is applied on the defined performance index.
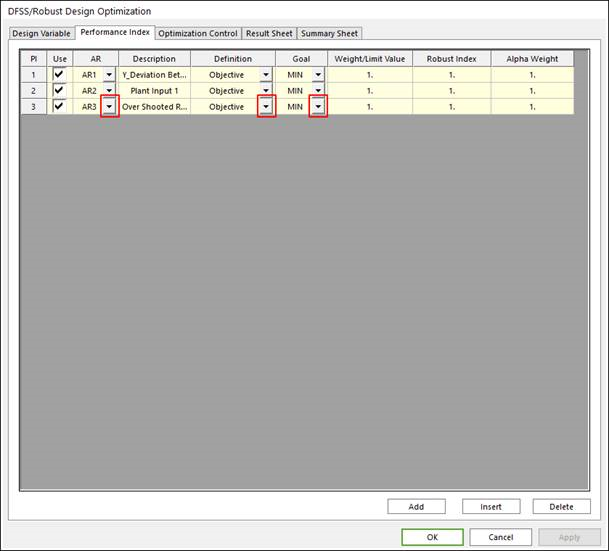
Figure 21.50 Performance Index tab of the DFSS/Robust Design Optimization dialog box
Select DOE and Meta modeling method, and polynomial function type.
This step is same in the case of design optimization problem.
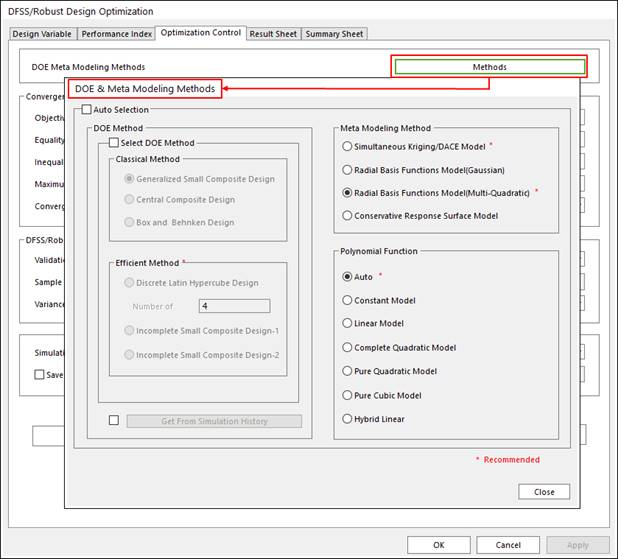
Figure 21.51 Select Method Options
Run optimization
Define convergence tolerance, DFSS/Robust design control and run robust design optimization. The run process is same as the case of design study process.
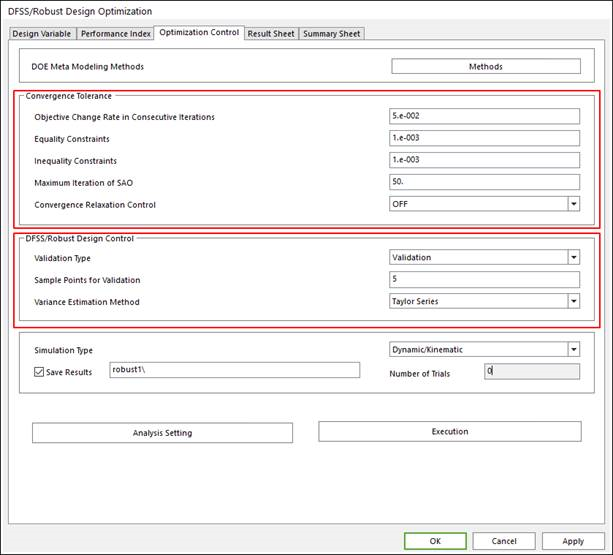
Figure 21.52 Optimization Control Dialog box
Convergence Tolerance: The definition is same as the case of design optimization. The guide for defining the convergence tolerance is in the Guides for Convergence Tolerance.
DFSS/Robust Design Control: Select the validation type as None, Validation, and Validation & Re-Optimization. None don’t need Sample Points for Validation definition. The guide for defining DFSS/Robust Design Control is explained in Validation of Robust Design and DFSS of Guideline.
21.2.3.5.2. Result Sheet of DFSS/Robust Design Optimization
In Result Sheet page, users can know the convergence history from the plotted curve. From the Optimization History of AR Values list, users can check the performance index results of each trial of optimization process. If users select Validation & Validation & Re-Optimization option in run optimization step, users can check and compare the estimated standard deviations to the sampled standard deviations. Or users can check the user defined robust index value and the relaxed robust index value. The guide for Validation option and the relaxed robust constraint is in the Guideline for AutoDesign manual.
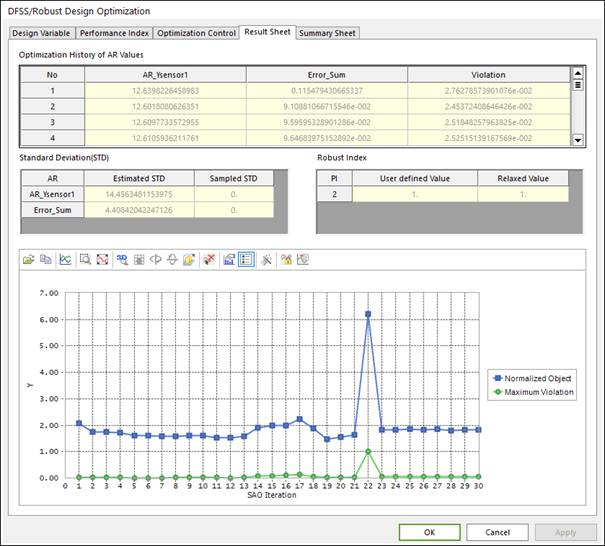
Figure 21.53 Result Sheet tab of the DFSS/Robust Design Optimization dialog box
21.2.3.5.3. Summary Sheet of DFSS/Robust Design Optimization
When the optimization is progressed, RecurDyn does not evaluate the same design values among the previous runs. This can save the computational time but make the final design results. Thus, the summary sheet window is provided as shown in Figure 21.54.
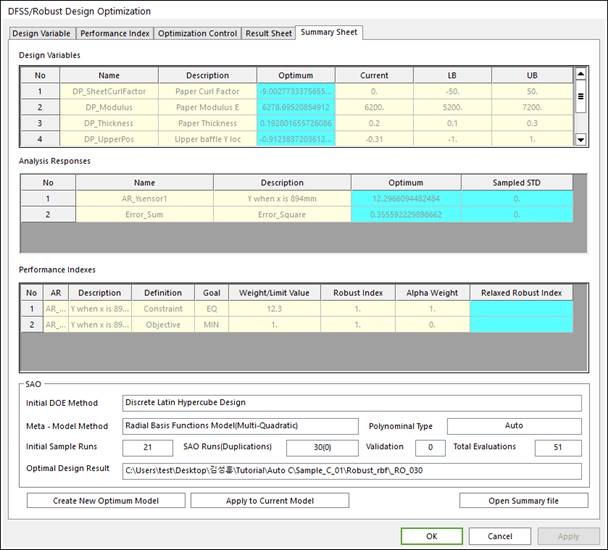
Figure 21.54 Summary Sheet tab of the DFSS/Robust Design Optimization dialog box
The summary sheet shows the optimum values of design variables and analysis responses. Also, the design optimization formulation is listed. Especially, it summarizes the SAO process, which includes DOE method, Meta-model method and total evaluations. Finally, it shows the analysis result file for the optimum design.