21.3.6.6. Validation of Robust Design and DFSS
In the window of optimization control shown in Figure 21.86, one can see DFSS/Robust Design Control unlike Design Optimization.
There are three options in Validation Type:
None
Validation
Validation & Re-Optimization
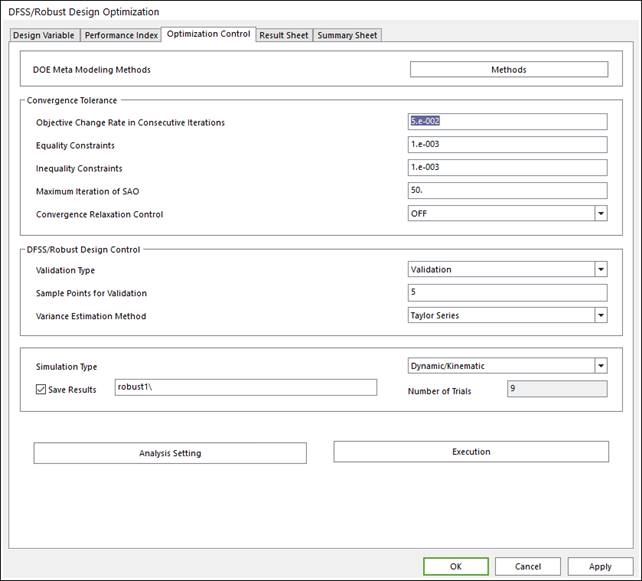
Figure 21.86 Optimization control window in DFSS/Robust Design Optimization
If one selects Validation or Validation & Re-Optimization, then he defines the number of sample points in Sample Points for Validation. Now, we explain the validation method.
First, AutoDesign evaluates the sample variance. Suppose that the number of sample points is defined as ‘10’. Then the sample variance is evaluated as
\(s{{\left( \mathbf{x} \right)}^{2}}=\frac{1}{N-1}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{N}{{{\left( f\left( {{\mathbf{x}}_{i}} \right)-\bar{f} \right)}^{2}}},\text{ }N=11\).
In this evaluation, the final design from SAO is automatically included. Hence, total number of is ‘\(N=10+1\)’. When sampling, AutoDesign uses Discrete Latin-hypercube.
When Validation or Validation & Re-Optimization is selected, AutoDesign check the violation of constraint using the sample standard deviation.
\({{g}_{j}}\left( \mathbf{x} \right)+{{k}_{j}}{{s}_{j}}\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\le \text{limit}\)
Sample |
Population |
Statistic |
Parameter |
Average = \(\bar{X}\) |
Mean = \(\mu(\bar{X}_0)\) |
Sample Standard Deviation = \(\varepsilon\) |
Standard Deviation = \(\sigma(s_0)\) |
If this condition is satisfied, then optimization is completed. Otherwise, all the sampled points are added to construct the meta-models. Then, restart optimization until converged or maximum iteration. However, if one selects just Validation, then AutoDesign is completed after evaluating the sample variance. In order to help one’s understand for sample variance, the concept of a population and a sample is compared in Table 21.4.