21.3.9.6. Guides for Reliability Analysis Method Selection
When the failure probability is much less than 0.1, Monte-Carlo simulation needs too many samples. Suppose that failure probability is 0.0001. Then, the estimated number of sampling is
\(N=396\text{ }\frac{1-0.0001}{0.0001}\)
Thus, if the estimated failure probability is too small, then we recommend that one tries to use SAO based Hybrid method. When one tries to use Monte-Carlo simulation, we recommend that he or she tries it by using 20 samples Latin Hypercube. Then, if the failure probability is obtained under 0.1 except 0.0, SAO method is recommended.
When mean value point lies too much away from PI=0 or standard deviation is too much small, shown in Figure 21.136, SAO based Hybrid method can’t find MPP. In other words, there is no point to satisfy PI=0 within the given range.
When this case occurs, one can see that all information does not changed until maximum iteration is reached in Result Sheet. Also, one can check this case in Summary Sheet. All AR values are greater than or less than their limits.
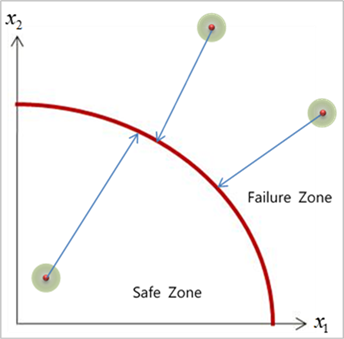
Figure 21.136 In case that SAO based Hybrid Method is failed
Even though all information is good, SAO based Hybrid method may be failed to converge due to the numerical noise of dynamic analysis. In this case, we recommend that one releases the convergence tolerance values in Analysis Control or that one tries to use Monte-Carlo simulation.