32.2.9. E.D.T(Equivalent Drive Train)
In the whole engine system, when a crankshaft is rotated, a resisting force is generated against the crank shaft caused by the EDT (Equivalent Drive Train), which is connected with a crank shaft. The EDT can include a transmission, clutch, drive shaft, chain, wheel, tire and so on. It is represented as relationship of components such as a EMI (Equivalent Moment of Inertia), stiffness including speed ratio, Drive and Driven body. In general, three types of EDT are used in automotive system. These are a direct-drive, gear-drive and belt-drive type.
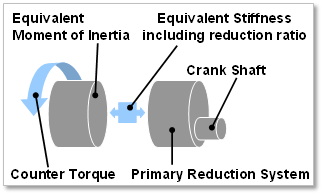
Figure 32.96 Direct Drive Type
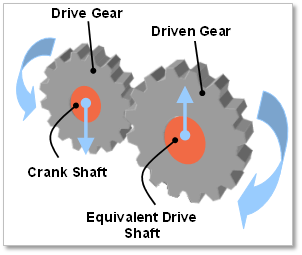
Figure 32.97 Gear Drive Type
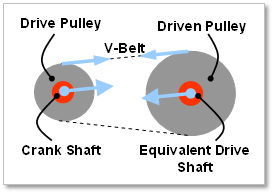
Figure 32.98 Belt Drive Type
32.2.9.1. Modeling Options
Click the EDT icon of the Crank group in the Crank tab. The user can see the Crank Component - EDT dialog box.
The user can select the position where a EDT is created in Component Index.
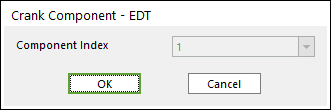
Figure 32.99 Crank Component - EDT dialog box
Click OK.