41.2.1. Tire Kinematics
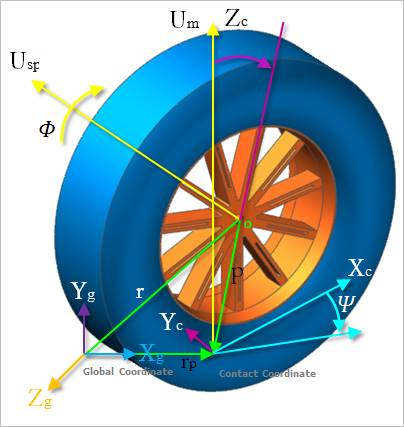
Figure 41.7 Tire Kinematics
Normal penetration depends on the normal direction of contact coordinate.
(41.1)\[\delta ={{r}_{2}}-{{r}_{pen}}\]
Where, \({{r}_{2}}\) is the carcass radius of toroidal and \({{r}_{pen}}\) is the contact radius from carcass center.
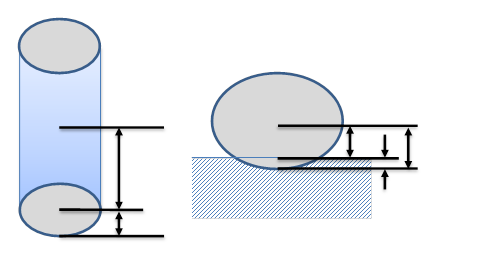
Figure 41.8 Normal Penetration
Inclination angle was defined \(\gamma\)
(41.2)\[\gamma =\frac{\pi }{2}-{{\cos }^{-1}}({{\mathbf{u}}_{sp}}\cdot {{\mathbf{u}}_{rn}})\]
The contact point position vector \({{\mathbf{r}}_{p}}\) was defined as following equation.
(41.3)\[{{\mathbf{r}}_{p}}=\mathbf{r}+\mathbf{\rho }\]
- where,
- \(\mathbf{r}\) is the position vector of tire.\(\mathbf{\rho }\) is the position vector from the tire center to contact point.
Also, the contact point velocity vector \({{\mathbf{v}}_{p}}\) is defined.
(41.4)\[{{\mathbf{v}}_{p}}=\frac{d}{dt}\mathbf{r}{}_{p}=\mathbf{r}+\mathbf{\omega }\times \mathbf{\rho }\]
(41.5)\[\mathbf{\omega }=\dot{\psi }{{\mathbf{z}}_{c}}+\dot{\gamma }{{\mathbf{x}}_{c}}+\varphi {{\mathbf{u}}_{sp}}\]
(41.6)\[{{\mathbf{u}}_{sp}}=-\cos (\gamma ){{\mathbf{y}}_{c}}-\sin (\gamma ){{\mathbf{z}}_{c}}\]
(41.7)\[\dot{\varphi }=\frac{\mathbf{\omega }\cdot {{\mathbf{u}}_{sp}}+\left( \mathbf{\omega }\cdot {{\mathbf{z}}_{c}} \right)\sin (\gamma )}{{{\cos }^{2}}(\gamma )}\]
(41.8)\[\dot{\gamma }=\mathbf{\omega }\cdot {{\mathbf{x}}_{c}}\]
(41.9)\[\dot{\psi }=\mathbf{\omega }\cdot {{z}_{c}}+\dot{\varphi }\sin (\gamma )\]
- Where,
- \(\mathbf{\omega }\) is the angular velocity vector of tire.\({{\mathbf{u}}_{sp}}\) spin direction unit vector.
The circumferential velocity of the contact point p, \({{v}_{cir}}\)
(41.10)\[{{v}_{cir}}=(\dot{\varphi }{{\mathbf{u}}_{sp}}\times \mathbf{\rho })\cdot {{\mathbf{x}}_{c}}\]
(41.11)\[{{v}_{xcir}}={{v}_{x}}+{{v}_{cir}}\]
(41.12)\[{{v}_{xcir}}={{\mathbf{v}}_{p}}\cdot {{\mathbf{x}}_{c}}\]
(41.13)\[{{v}_{x}}={{v}_{xcir}}-{{v}_{cir}}\]
The lateral slip velocity of the contact point p, \({{v}_{y}}\)
(41.14)\[{{v}_{y}}={{\mathbf{v}}_{p}}\cdot {{\mathbf{y}}_{c}}\]
The normal penetration velocity, \({{v}_{pen}}\),
(41.15)\[{{v}_{pen}}={{\mathbf{v}}_{p}}\cdot {{\mathbf{z}}_{c}}\]