33.2.1. Engine Block
An engine block is composed of a single body. The shape of engine block is automatically determined by other parameters.
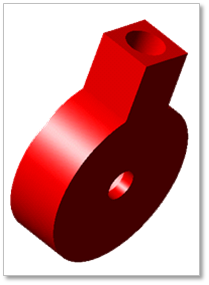
Figure 33.12 Engine Block
33.2.1.1. Modeling Options
Click the E.Block icon of the Piston group in the Piston tab. The user can see the Crank Component - EBlock dialog box.
The position of an engine block is automatically defined.
Only one engine block should exist at the current system.
If an engine block already exists, the user cannot create engine block anymore.
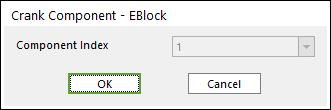
Figure 33.13 Crank Component - EBlock dialog box
Click OK.
33.2.1.2. Properties
Click the right mouse button on the engine block body to choose Properties of the engine block. The user can modify the property of engine block in the following dialog.
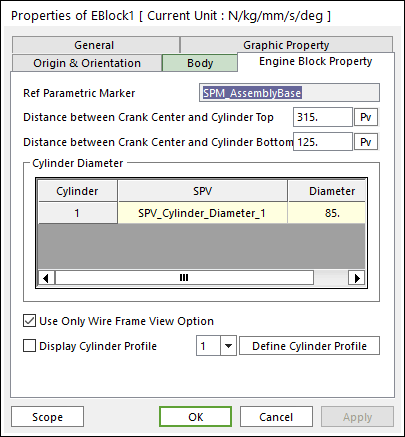
Figure 33.14 Engine Block proper page
Reference Parametric Marker: Controls the position of engine block. It is also special parametric marker (SPM).
Distance between Crank Center and Cylinder Top/Bottom: Refer to Figure 33.15.
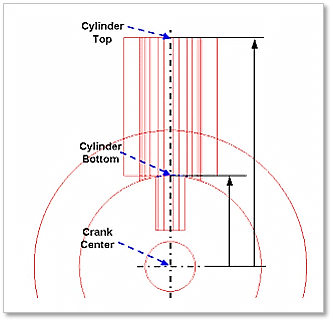
Figure 33.15 Distance between Crank Center and Cylinder Top/Bottom
Cylinder Diameter: Is also the special parametric value. The user can modify the parametric value in this section.
These values are enlisted in the special parametric value list.
The name and value of each parameter are shown.
Use only wire frame view: If it is checked, an engine block is displayed only in the wire frame mode even though the whole view option is the shade mode. It is useful to see the inner motion of engine block.
Display Cylinder Profile: If it is checked, it is possible to confirm the cylinder profile associated with the contact between the cylinder and the piston.
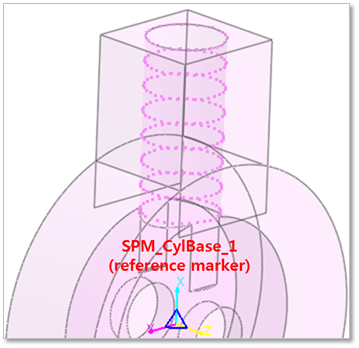
Figure 33.16 Display Cylinder Profile
Define Cylinder Profile: Changes the values to define the cylinder profile which is based on SPM_CylBase_i (reference marker). Refer to the following example.
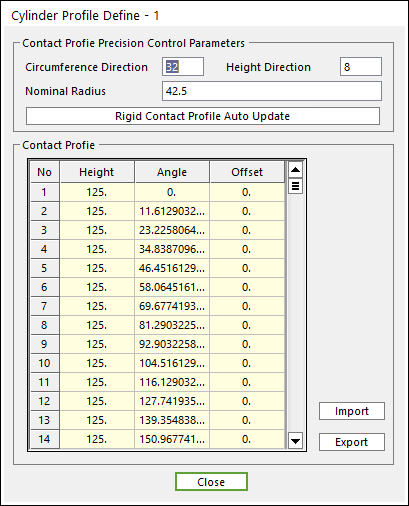
Figure 33.17 Cylinder Profile Definition dialog box
To modify the values such as Nominal Radius, Angle and Height, the user should change values (Nominal Radius and Angle) related with the circumference direction, and then change the value (Height) related with the height direction.
Enter the values of Circumference Direction / Height Direction (ex, 3, 2) and then click Rigid Contact Profile Auto Update. And the user can confirm the Cylinder Profile which is based on SPM_CylBase_i (reference marker) .
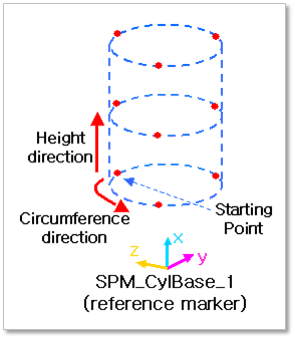
Figure 33.18 An example of Display Cylinder Profile