21.3.6. Guides for Robust Design and DFSS
In conventional optimization problems, the objective is to minimize or maximize linear or non-linear functions of design variables subject to a set of constraints. In contrast, robust design optimization tries to optimize not only the function value but also its sensitivity due to the variation of the design variables or noise parameters. Figure 21.80 illustrates the concepts of robust design optimization for an unconstrained design space.
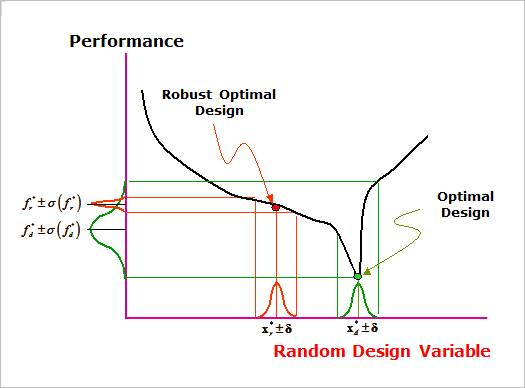
Figure 21.80 Robust optimal design for unconstrained optimization problem
Suppose that the design variables have variation \(\mathbf{\delta }\) due to manufacturing error or tolerance. If one doesn’t consider the effect of the variation \(\mathbf{\delta }\) in his or her design, a typical optimizer minimizes or maximizes only the performance. Then, it is not guarantee that its optimal design \(\left( \mathbf{x}_{d}^{*} \right)\) does not make its objective value \(\left( f_{d}^{*} \right)\) be insensitive to the variation \(\mathbf{\delta }\). In order to solve these problems, AutoDesign provides Robust design optimization and Design For Six-Sigma (DFSS).